ClinVar
has documented total 139 variants of clinical significance reported regarding
the PAH gene. Total 612 results showed up on the screen. There are 85
pathogenic variants, while 40 variants are likely pathogenic, five variants
were of uncertain significance, 5 are benign and 4 are likely to be benign. The
review status was submitted for all the 85 pathogenic variants of clinical significance.
70 submissions were done single handedly while multiple reviewers or
researchers worked together and made 15 submissions.
Out of 15 submissions 14 had literature review and clinical testing , while only one had literature review only. 70
clinical variants of pathogenic origin are handled single handedly by
researchers. While 20 researchers did literature review and the clinical testing
49 researchers presented the literature review only.
–Document how many labs provide tests
related to your gene.
The pathogenic variant of PAH gene can present in the form of phenylalanine hydroxylase deficiency which if severe will lead to inability of the person to utilize essential amino acid phenylalanine in body and its break down into tyrosine leading to phenylketonuria (PKU) which if not diagnosed early will lead to brain damage. Other pathologic variant can also lead to non-phenylketonuria hyperphenylalaninemia (Non-PKU HPA) and variant PKU.
The
blood is taken from the heel of the baby called the heel stick test and the phenylketonuria-screening
test is done within 24 hrs. of birth of baby to find out the absence of
Phenylalanine hydroxylase in order to prevent the excessive accumulation of
phenylalanine that in excess can cause brain damage.
The Genetic Testing
Registry (GTR) offer 87 clinical tests for PKU. 44 clinical tests are used for
diagnosis, 23 for mutation confirmation, 11 pre-symptomatic, 4 for monitoring
and 1 for therapeutic management and 1 for drug response. The sequencing
analysis of entire coding region is done along with the deletion/insertion
analysis and the variant analysis, full panel quantitative random urine
analysis for organic acids, amino-acid analysis of plasma is done is done for
the diagnosis of PKU and for mutation confirmation. For the diagnosis and monitoring of PKU the
quantitative analysis of phenylalanine and tyrosine is done.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/gtr/conditions/C0031485/
–Use DNAStar to simulate RFLP.
–Use DNAStar to simulate RFLP.
The
first clinically significant variant shown by the ClinVar shows the single
point mutation at the position 781. The C > G and the amino acid Arginine is
replaced by Glycine. This mutation does not bring about the change in the
neighboring restriction enzymes. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/clinvar?term=612349%5BMIM%5D
 |
| PAH- 781 (C)Arginine |
 |
| PAH- 781 (G)Glycine |
 |
| PAH- 781 (C)Arginine The restriciton enzyme BbsI & BbsgI |
 |
| PAH- 781 (G) Glycine. The restriciton enzyme BbsI & BbsgI |
Many disease associated variants create or destroy restriction enzyme recognition sites. My
gene PAH has the allelic variant 0.0002 in OMIM. It is SNP and a point mutation
the nucleotide at the position 222 CGG-TGG in exon 12. This mutation will
result in the replacement of amino acid Arginine by tryptophan at the position
408. This is a clinically significant variant.
 |
| PAH-gene-1224-CGG-Arginine & enzyme NmeAIII
|
 |
| PAH-gene-1224-CGG-Arginine |
 |
| PAH-gene-1224-TGG-Tryptophan & enzyme NmeAIII is not seen |
 |
| The restriction enzyme NmeAIII in PAH gene |
GeneQuest simulation of the agarose gel run with the DNA sequence by the enzyme NmeAIII.
 |
| The PAH-gene shows the one cut by NmeAIII enzyme |
 |
| The PAH-allele (R-408-W) shows no cut by NmeAIII enzyme |
 |
| The PAH-gene shows the one cut by NmeAIII enzyme |
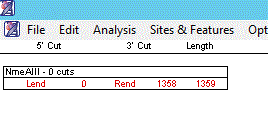 |
| The PAH-allele shows no cut by NmeAIII enzyme |
Conclusion:
Allelic variant of my gene PAH from ClinVar NM_000277.1(PAH):c.781C>G(p.Arg261Gly)
did not show the loss of sites of Restriction Enzyme BbsI and BbsgI.
Allelic variant of gen PAH 0.0002 in OMIM is recognized in ClinVar NM_000277.1(PAH):c.1222C>T (p.Arg408Trp) resulted in the loss of the site for restriciton enzyme NmeAIII.

No comments:
Post a Comment