A narrative blog post which includes an
original description of the allele and a discussion of the impact of the change
on the predicted secondary structure.
0.0001 PHENYLKETONURIA
PAH,
IVS12DS, G-A, +1
The
first PKU mutation identified in the PAH gene was a single base change
(GT-to-AT) in the canonical 5-prime splice donor site of intron 12.
Since the variant/allele 0.0001 is due to the single
base change in the site of intron 12, I picked the allele 0.0002 and discussed
the impact on the predicted secondary structure.
0.0002 PHENYLKETONURIA
PAH,
ARG408TRP
This defect is caused by a CGG-to-TGG transition in
exon 12, resulting in an amino acid substitution (arg-to-trp) at residue 408
(R408W) of PAH.
This mutation makes up about 20% of the mutant PAH
genes. It is one of the examples of CpG mutation. The R408W mutation occurs
within the catalytic domain of PAH. PAH with the R408W mutation formed
high-molecular-mass aggregates, indicative of severe distortion of the
protein's oligomeric state.
I opened the mRNA sequence of my PAH gene in the seq-builder and highlighted the open reading frame of the gene beginning with the ATG codon of methionine. I highlighted the ORF in the upper strand and translated it into the protein sequence and saved it.
Since the allelic/variant is the change in the amino acid Arginine to(R) to tryptophan (W), I opened the protein sequence in the edit seq made the change and saved it under the name of PAH-allele(R408W).
The Arginine is a basic amino acid and tryptophan is a hydrophobic amino acid thus I expect to see changes in the secondary structure.
The protein statistics in the edit-seq about the PAH-gene and the PAH-allele is different in the molecular weight, isoelectric point to PH.
The PAH-gene Protein statistics.
Molecular Weight 51862.15 Daltons
452 Amino Acids
54 Strongly Basic(+) Amino Acids (K,R)
60 Strongly Acidic(-) Amino Acids (D,E)
155 Hydrophobic Amino Acids (A,I,L,F,W,V)
119 Polar Amino Acids (N,C,Q,S,T,Y)
6.408 Isolectric Point
-4.147 Charge at PH 7.
Protein Info about pah-allele-R-W.pro(1,453)
Molecular Weight 51892.17 Daltons
452 Amino Acids
53 Strongly Basic(+) Amino Acids (K,R)
60 Strongly Acidic(-) Amino Acids (D,E)
119 Polar Amino Acids (N,C,Q,S,T,Y)
6.293 Isolectric Point
-5.147 Charge at PH 7.0
I opened the mRNA sequence of my PAH gene in the seq-builder and highlighted the open reading frame of the gene beginning with the ATG codon of methionine. I highlighted the ORF in the upper strand and translated it into the protein sequence and saved it.
Since the allelic/variant is the change in the amino acid Arginine to(R) to tryptophan (W), I opened the protein sequence in the edit seq made the change and saved it under the name of PAH-allele(R408W).
The Arginine is a basic amino acid and tryptophan is a hydrophobic amino acid thus I expect to see changes in the secondary structure.
The protein statistics in the edit-seq about the PAH-gene and the PAH-allele is different in the molecular weight, isoelectric point to PH.
The PAH-gene Protein statistics.
Molecular Weight 51862.15 Daltons
452 Amino Acids
54 Strongly Basic(+) Amino Acids (K,R)
60 Strongly Acidic(-) Amino Acids (D,E)
155 Hydrophobic Amino Acids (A,I,L,F,W,V)
119 Polar Amino Acids (N,C,Q,S,T,Y)
6.408 Isolectric Point
-4.147 Charge at PH 7.
Protein Info about pah-allele-R-W.pro(1,453)
Molecular Weight 51892.17 Daltons
452 Amino Acids
53 Strongly Basic(+) Amino Acids (K,R)
60 Strongly Acidic(-) Amino Acids (D,E)
119 Polar Amino Acids (N,C,Q,S,T,Y)
6.293 Isolectric Point
-5.147 Charge at PH 7.0
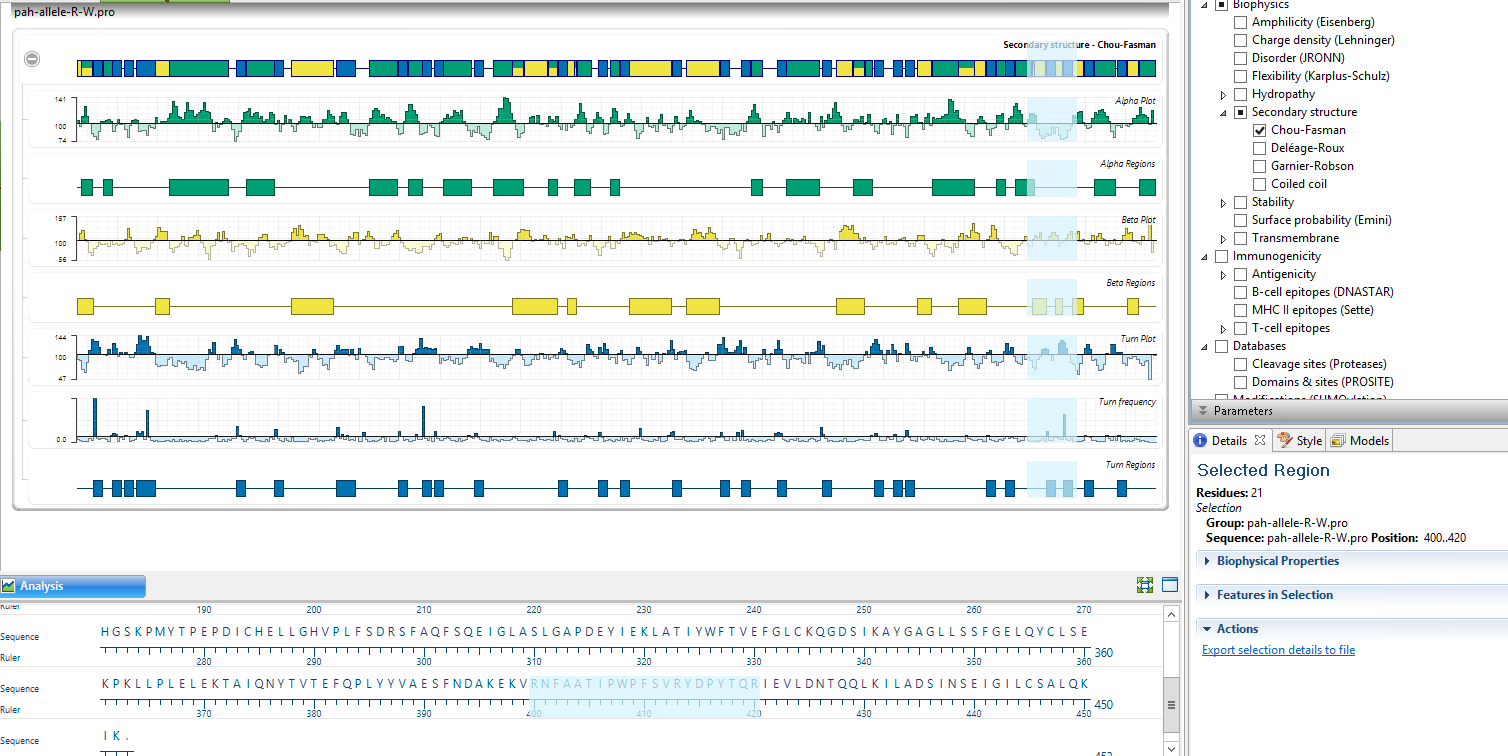
The
changes seen in the Protean of DNASTAR are as following:
The Beta Regions from the amino acid 400 till the
end of the secondary structure as depicted by the Garnier-Robson and Chou-
Fasman algorithm. The turn regions by the
Chou-Fasman algorithm. The coil region by the Garnier-Robson algorithm the
alpha amphipathic region and the Beta Amphipathic region as well as the
flexible regions by Karplus-Schulz algorithm.
I have observed changes in the Apha, beta coil and turn regions by the Chou-Fasman and Garnier-Robonson as seen in the zoomed version of the Protean in DNASTAR.
I have observed changes in the Apha, beta coil and turn regions by the Chou-Fasman and Garnier-Robonson as seen in the zoomed version of the Protean in DNASTAR.
-Protean000.gif) |
| The PAH-gene-&&-PAH-allele(R408W) |
The detalied comparison of the PAH gene and its allele with
(R408W) in Protean.
Secondary Structure - Chou-Fasman—Predicts secondary structure of proteins from the crystallographic structures of their mino acid sequences.
The
changes seen in the region from amino acid 400 to the end of the polymer for
the PAH gene and the allele variant in Protean. The Amino Acids from 400 to 420 are highlighted.
 |
| PAH-gene-400-420AA |
-zoomed-400-420AA.gif) |
| PAH-allele(R408W)-400-420AA |
The secondary structure changes as seen in the Protean 3D of DNASTAR in the PAH-gene and PAH-alllele (R408W).
Secondary Structure -
Garnier-Robson—Examines the propensity of a given
residue to exist in a certain structure.
I observed the changed in the beta regions, turn regions and coil regions in PAH-gene and allele but no change in the alpha regions.
 |
| PAH-gene-400-420AA-highlighted |
 |
| PAH-allele(R408W)-400-420AA-highlighted . |
I did not observe any change in the secondary structure PAH-gene and its allele.
 |
| PAH-gene-400-420AA-highlighted |
 |
| PAH-allele(R408W)-400-420AA-highlighted |
Hydropathy - Kyte-Doolittle—Predicts regional hydropathy of proteins from their amino acid sequences.
The hydrophicity and the hydrophobic regions were different in the PAH_gene and its allele (R408W) as expected. No change was noticed in the hydrophilic regions.
The hydrophicity and the hydrophobic regions were different in the PAH_gene and its allele (R408W) as expected. No change was noticed in the hydrophilic regions.
 |
| PAH-gene-400-420AA-highlighted |
 |
| PAH-allele(R408W)-400-420AA-highlighted |
Hydropathy - Hopp-Woods—Finds protein antigenic determinants by searching protein sequences for the area of greatest local hydrophilicity.
The hydrophicity and the hydrophobic regions were different in the PAH_gene and its allele (R408W) as expected. No change was noticed in the hydrophilic regions.
The hydrophicity and the hydrophobic regions were different in the PAH_gene and its allele (R408W) as expected. No change was noticed in the hydrophilic regions.
 |
| PAH-gene-400-420AA-highlighted |
 |
| PAH-allele(R408W)-400-420AA-highlighted |
Antigenicity- Jameson-Wolf—Predicts potential antigenic determinants by combining existing methods for protein structural predictions.
The antigenicity regions of the two structure are also different.
The antigenicity regions of the two structure are also different.
 |
| PAH-gene-400-420AA-highlighted |
 |
| PAH-allele(R408W)-400-420AA-highlighted |
Amphiphilicity – Eisenberg—Predicts the Eisenberg Moment.
Due to the incorporation of the hydrophobic amino acid tryptophan in the allelic variant the Amphilicity of the PAH-gene and its allele was different in the Hydrophobicity plot, Alpha amphipathic and Beta amphipathic region and Alpha and Beta moment.
 |
| PAH-gene-400-420AA-highlighted |
 |
| PAH-allele(R408W)-400-420AA-highlighted |
Surface Probability – Emini—Predicts the probability that a given region lies on the surface of a protein. The surface probability for the region between the amino acid 400 to 420 for the PAH-gene and PAH-allele (R408W) was also changed.
 |
| PAH-gene-400-420AA-highlighted |
 |
| PAH-allele(R408W)-400-420AA-highlighted |
Flexibility - Karplus-Schulz—Predicts backbone chain flexibility.
The PAH-gene and its mutant had different flexibility plots in the region of Amino Acids 400 to 420.
 | |||||||
| PAH-gene |
 |
| PAH-allele(R408W) |
Even the stability of the two structure showed difference in their plots in the amino acid 400-420 region.
 | |||
| PAH-gene |
 |
| PAH-allele |
Thus I observed marked differences in the secondary structure of the PAH gene and its allele (R408W) in the Amino Acid regions from 400 to 420 amino acids.
No change was observed in the transmembrane property between the PAH-gene and its allele.
 | |||
| PAH-gene |
 |
| PAH-allele |
The vocabulary used in the description of the gene
and allele
Linkage
disequilibrium
The nonrandom association between two or more
alleles such that certain combinations of alleles are more likely to occur
together on a chromosome than other combinations of alleles
In other words, linkage disequilibrium is the
occurrence of some combinations of alleles or genetic markers in a population
more often or less often than would be expected from a random formation of
haplotypes from alleles based on their frequencies.
Haplotype
A haplotype is a set of DNA variations, or
polymorphisms, that tend to be inherited together. A haplotype can refer to a
combination of alleles or to a set of single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs)
found on the same chromosome.
Oligomer
A
polymer that consists of two, three, or four monomers.
A
monomer may combine with another monomer through chemical bonds to form a
larger molecule, as in a polymer.
Examples
of monomers are amino acids that link together by a peptide bond forming a
polypeptide or protein.
-Protean.gif)
No comments:
Post a Comment